| CE.2 – American Constitutional Democracy: Structure and Powers of Government (new 2023 standards) |
|---|
CE.2a The Three Branches of Government
The national government has three main parts, or branches:
Each branch has different responsibilities and powers, and they must work together to run the country fairly and effectively. CE.2b The Legislative Branch (Article I)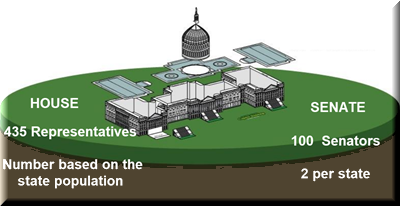
Article 1 of the Constitution establishes the Legislatiave Branch. This branch is called Congress, and it's made up of two parts :
Together, they make up a bicameral legislature—“bi” means two, and “camera” means chamber. Congress is responsible for writing and passing laws.
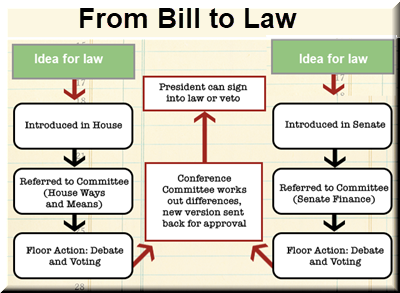
In addition to making laws, the Legislative Branch also:
Artlicle 1 of the Constitution gives Congress both expressed and implied powers.
CE.2c The Executive Branch (Article II)
Article II of the Constitution establishes the Executive Branch. This branch is led by the President of the United States, who serves as:
The Vice President, Cabinet, and many federal agencies (like the FBI or the Department of Education) help the President carry out these responsibilities and execute the laws. Ways the executive branch influences policymaking
CE.2d The Judicial Branch (Article III)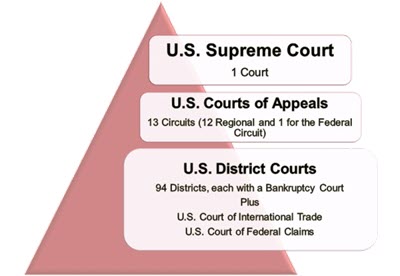
Article III of the Constitution establishes the Judicial Branch.
Congress decides how many judges serve and how the court system is organized, but the Constitution requires there be one Supreme Court. The main job of the courts is to settle disputes and make sure that laws and actions are constitutional—this is called judicial review. CE.2e Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances
Articles I, II, and III of the Constitution define the powers of the three branches of government. The Constitution divides power between these three branches so no one group gets too powerful. This is called separation of powers. Each branch also has the ability to limit or “check” the power of the other branches. This is called the system of checks and balances. Examples:

Bill of Rights

Due Process
Judicial Review
|